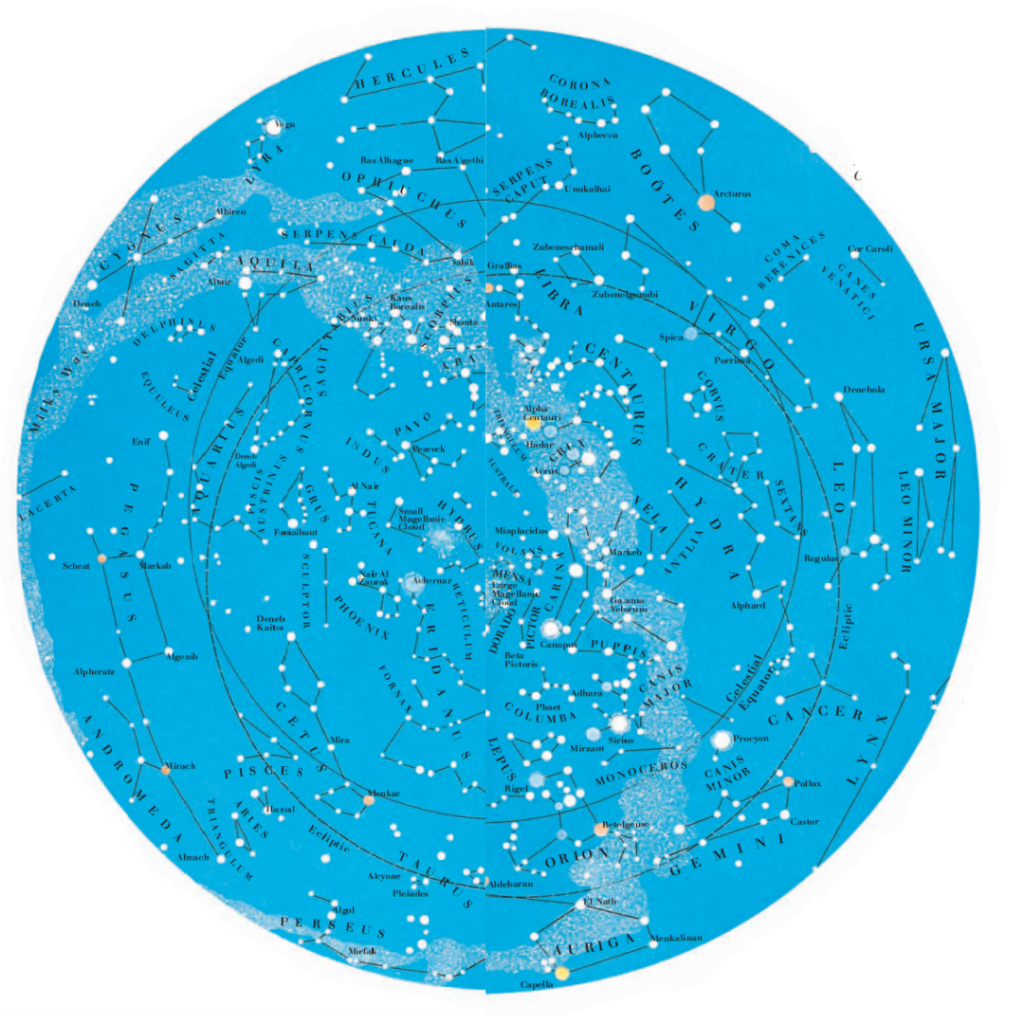
WHEN YOU LOOK AT THE SOUTHERN SKY, you look toward the Galactic center, which has a huge population of stars. As a result, the Milky The way appears brighter in the southern sky than in the northern sky. The southern sky is rich in nebulae and star clusters. It contains the Large and Small Magellanic Clouds, which are two of the nearest galaxies to our own.

Stars make fixed patterns in the sky called constellations. However, the constellations are only apparent groupings of stars, since the distances to the stars in a constellation may vary enormously. The shapes of constellations may change over many thousands of years due to the relative motions of stars. The movement of the constellations across the sky are due to the Earth’s motion in space. The daily rotation of the Earth causes the constellations to move across the sky from east to west and the orbit of The earth around the Sun causes different areas of the sky to be visible in different seasons. The visibility of areas of the sky also depends on the location of the observer. For instance, stars near the celestial equator may be seen from either hemisphere at some the time during the year, whereas stars close to the celestial poles (the celestial The South Pole is at the center of the map shown here) can never be seen from the opposite hemisphere.









